Acidity in Tea Leaves Chemistry Investigatory Project PDF Class 12

Introdcution
Tea is a popular beverage made by infusing dried tea leaves or herbs in hot water. The leaves used to make tea come from the Camellia sinensis plant, and the processing methods applied to these leaves determine the type of tea produced. There are several main types of tea, including green tea, black tea, white tea, and oolong tea, each with its own distinct flavour, aroma, and colour.
The preparation of tea involves steeping the tea leaves or tea bags in hot water, allowing the flavours and compounds from the leaves to be released into the liquid. The brewing time, water temperature, and other factors can influence the taste of the tea. Beyond the traditional teas, there are also herbal teas made from infusing various plants, flowers, or herbs in hot water.
Tea has been enjoyed for centuries and holds cultural significance in many societies. It is not only valued for its diverse flavours but also for the potential health benefits associated with its antioxidant content. Whether sipped for relaxation, socializing, or health reasons, tea remains a globally beloved and versatile beverage.
Contents of Tea
Tea contains catechins, a type of antioxidant. In a freshly picked tea leaf, catechins can comprisal up to 30% of the dry weight. Tea also contains L-theanine, and the stimulant caffeine at about 3% of its dry weight, translating to between 30 mg and 90 mg per 250 ml cup depending on type, brand, and brewing method. Tea also contains small amounts of theobromine and theophylline. Due to modern environmental pollution, fluoride and aluminium have also been found to occur in tea, with certain types of brick tea made from old leaves and stems having the highest levels. This occurs due to the tea plant’s high sensitivity to and absorption of environmental pollutants.
Reason for Acidity in Tea Leaves
The acidity in tea leaves is primarily attributed to the presence of natural organic acids. One of the key acids found in tea leaves is citric acid, although other acids such as oxalic acid and malic acid may also contribute to the overall acidity. These acids play a crucial role in shaping the flavour profile of the tea. The levels of acidity can vary depending on factors such as the tea plant variety, growing conditions, and processing methods. Additionally, the terroir of the tea-growing region, including factors like soil composition and climate, can influence the acidity of the tea leaves. During the growth and development of the tea plant, environmental factors and the plant’s metabolic processes contribute to the accumulation of these organic acids. The acidity in tea leaves contributes to the refreshing and lively taste that is characteristic of many types of tea, and it is a key element in the complex interplay of flavours that tea enthusiasts appreciate.
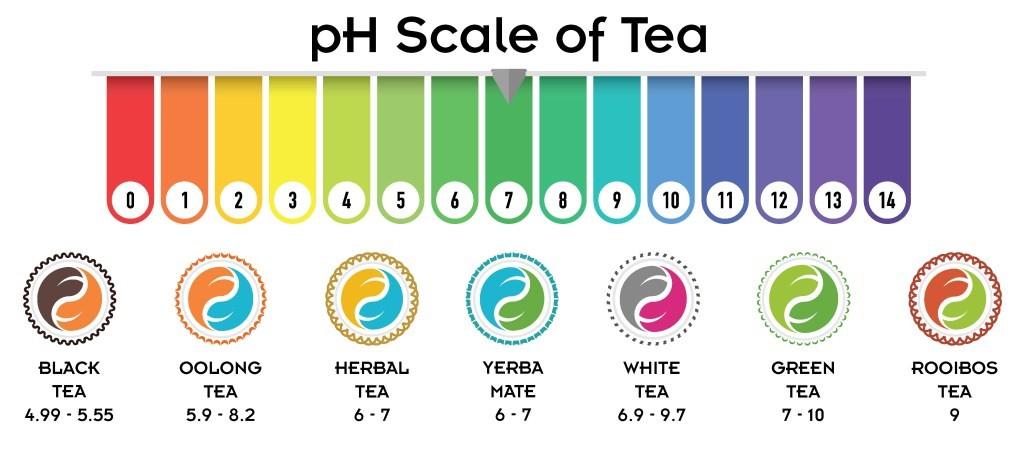
Factors Affecting Amount of Oxalic Acid in Tea Leaves
The amount of oxalic acid in tea is influenced by various factors related to the tea plant, processing methods, and brewing practices. Oxalic acid is a naturally occurring organic acid found in many plants, including tea leaves. Here are several factors that can affect the amount of oxalic acid in tea:
- Tea Plant Varieties:
Different tea plant varieties contain varying levels of oxalic acid. For example, Camellia sinensis var. sinensis (Chinese tea plant) and Camellia sinensis var. assamica (Assam tea plant) may have different oxalic acid concentrations. - Growing Conditions:
Soil composition and environmental factors, such as climate and altitude, can influence the accumulation of oxalic acid in tea leaves. Plants may produce more oxalic acid as a response to stress, such as nutrient deficiencies or environmental challenges. - Leaf Position:
Oxalic acid levels can vary in different parts of the tea plant. Young leaves and buds may contain higher concentrations of oxalic acid compared to older leaves. - Processing Methods:
The methods used to process tea leaves can affect the oxalic acid content. Oxalic acid is water-soluble, so the extent to which tea leaves are oxidized, fermented, or undergo other processing steps can influence the final oxalic acid concentration in the tea. - Brewing Time and Temperature:
The brewing process can impact oxalic acid levels in the tea infusion. Extended brewing times and higher water temperatures may lead to greater extraction of oxalic acid from the tea leaves. - Tea Grade and Quality:
Higher-quality teas, which often consist of young and tender leaves, may contain higher levels of oxalic acid. The processing methods used for premium teas may also affect oxalic acid concentrations. - Geographical Origin:
The geographical region where tea is grown can influence its chemical composition, including oxalic acid content. Different growing conditions and soil types contribute to regional variations in tea characteristics. - Cultivation Practices:
The use of fertilizers, pesticides, and other cultivation practices can impact the chemical composition of tea leaves, including oxalic acid levels. - Leaf Maturity:
As tea leaves mature, the oxalic acid content may change. Young leaves and buds may have higher oxalic acid concentrations compared to older, fully developed leaves.
Aim
To compare the oxalic acid content in the various samples of Tea leaves.
Requirements
- 5gm of three different brands of tea leaves
- Calcium Carbonate (CaCO3)
- Filter Paper
- Funnel
- Beaker
- Chemical Balance
- Wire Gauge
- Tripod Stand
- Bunsen Burner
Theory
- Tea contains catechins, a type of antioxidant. In a freshly picked tea leaf, catechins can comprisal up to 30% of the dry weight.
- Tea also contains L-threonine, and the stimulant caffeine at about 3% of its dry weight depending on the type, brand and brewing method.
- Tea also contains small amounts of the bromine and theophylline. Due to modern environmental pollution, fluoride and aluminium have also been found to occur in tea.
- Tannic Acid in tea is actually a myth, a rather popular one. The acidity of tea leaves is not due to the tannic acid. Tea contains polyphenols or catechins which are a specific type of tannin.
- The oxalic acid present in the tea leaves is precipitated as calcium oxalate by treatment of aqueous solution of tea with calcium carbonate. Calcium oxalate is then hydrolysed with conc. H2SO4 and recrystallized from water.

Procedure
- Weigh exactly 10gm of 1st sample of tea leaves.
- Take 200ml of distilled water in a beaker.
- Put tea leaves in above beaker boil it for 10 minutes.
- Filter above boiled solution using funnel and filter paper in another beaker.
- In filtrate add 4gms of CaCO3 and boil it.
- Filter above boiled solution using funnel and filter paper in another beaker. There will be a precipitation of Calcium oxalate on the filter paper.
- Keep filter paper aside and let it dry.
- Weigh the ppt. of oxalic acid.
- Repeat the above steps for the other two samples
Observation
S. NO | Brand of Tea | Weight of Tea Leaves | Weight of Acid Obtained | Percentage of Oxalic Acid |
1 | Red Label | 10gm | 0.91 | 9.1% |
2 | Twinings | 10gm | 0.97 | 9.7% |
3 | Taj Mahal | 10gm | 0.80 | 8% |
Result
The results indicate variations in the oxalic acid content among the different tea brands. Twinings exhibited the highest percentage of oxalic acid at 9.7%, followed closely by Red Label at 9.1%. Taj Mahal, on the other hand, showed a slightly lower percentage at 8%.
These differences may arise from various factors such as tea plant varieties, growing conditions, and processing methods unique to each brand.
Conclusion
In conclusion, this investigatory project aimed to compare the oxalic acid content in different samples of tea leaves from Red Label, Taj Mahal, and Twinings. The results revealed varying percentages of oxalic acid, with Twinings exhibiting the highest amount at 9.7%. The procedure involved boiling tea leaves, precipitating oxalic acid with calcium carbonate, and determining the weight of the obtained acid.
While the investigation provided insights into oxalic acid levels, it’s important to note that the presence of oxalic acid in tea is influenced by multiple factors, including tea plant variety, growing conditions, processing methods, and brewing practices. Furthermore, the project highlighted the potential health benefits of consuming tea, such as its antioxidant properties, heart health benefits, weight management support, and more.
Precaution
- Use precise measurements when weighing tea leaves and chemicals to ensure accurate results.
- Ensure the cleanliness of all equipment, especially the beakers, funnels, and filter paper, to prevent contamination.
- Boil the tea leaves for the specified duration (10 minutes) to extract the desired components effectively.
- Handle boiling water and hot apparatus with care to avoid burns or accidents.
- Conduct the experiment in a well-ventilated area to avoid inhaling potentially harmful fumes.
- Allow the filter paper with the precipitated calcium oxalate to dry thoroughly before weighing to prevent errors in the measurement.
- Repeat the experiment for each tea sample to ensure the reliability of the comparative analysis.
- Dispose of waste materials properly, following appropriate laboratory waste disposal procedures.

