Electroscope Physics Investigatory Project PDF Class 12

Introduction
What is Electroscope?
Electroscope, is an instrument used for detecting the presence of an electric charge or of ionizing radiation, usually consisting of a pair of thin gold leaves suspended from an electrical conductor that leads to the outside of an insulating container.
- An electric charge brought near the conductor or in contact with it causes the leaves to stand apart at an angle because, according to Coulomb’s law, the like electric charge either induced in or transferred to each leaf causes them to repel each other.
- Radiation from radioactive materials introduced into a charged electroscope ionizes the gas within, permitting the charge on the leaves to leak off gradually. The rate at which the leaves of a charged electroscope converge to their parallel uncharged position is proportional to the intensity of radiation present.
Types of Electroscope
In general, the electroscopes are classified into the following three types:
- Pith-ball Electroscope:
As the name suggests, it consists of one or two small balls that are made up of a lightweight non-conductive substance and known as pith. To determine whether the object is charged or not by using this electroscope, the object is brought close to the uncharged pith-ball. The force of attraction between the ball and object shows that the object is charged. - Gold-leaf Electroscope:
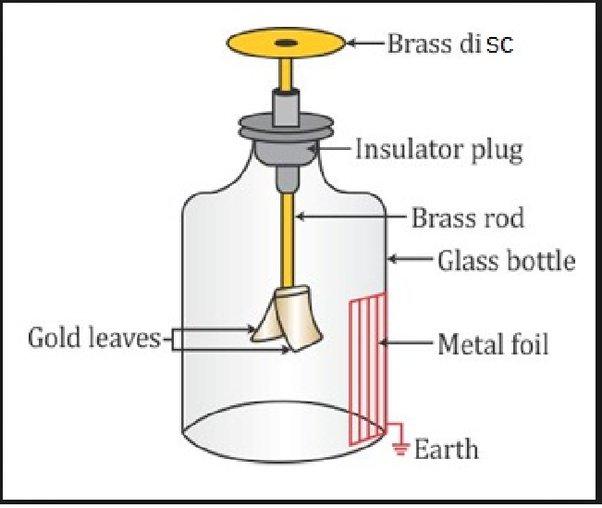
It consists of a vertical conductive rod with a metal ball on the top and two thin and parallel strips of gold leaf attached at the bottom. Invented by Abraham Bennet in 1787, this electroscope is comparatively more sensitive than a pith-ball one. To prevent the gold leaf from drafts of air, it is kept in a glass bottle. The gold leaves, which are kept in a glass flask to prevent them from the effect of air, spread apart into inverted “V” whenever a charged object is brought close to them. - Needle Electroscope:
It consists of a plate connected to a support stand and a pivoted free-swinging needle on either side of the stand. If a charged object is brought near to the plate, then the needle will gain the same charge and will swivel away.
Use of Electroscope
Following are some common uses of an electroscope:
- Detecting Electric Charges:
Electroscopes are primarily used to detect the presence of electric charges. When an object with an electric charge (either positive or negative) is brought near the conducting ball or plate of the electroscope, the leaves will either repel or attract each other, indicating the presence and type of charge. - Demonstrating Static Electricity:
Electroscopes are often used in educational settings to demonstrate static electricity phenomena. For example, you can rub a balloon against your hair to create static charge and then bring it close to the electroscope to show the leaves diverge due to the charge transfer. - Measuring Electric Potential:
Electrometers, which are more sensitive versions of electroscopes, can be used to measure electric potential (voltage). By calibrating an electrometer, you can determine the voltage of an electrical source. - Testing for Grounding:
An electroscope can be used to check if an object is grounded. If an object is grounded, the electroscope’s leaves will collapse because the charge is dissipated into the Earth. If an object is not grounded, the leaves will remain diverged. - Monitoring Radiation:
Some radiation detection devices use an electroscope or a similar instrument to detect and measure ionizing radiation. When radiation interacts with the air, it can create charged particles that affect the electroscope’s leaves. - Historical Experimentation:
Electroscopes have played a significant role in the history of electricity and have been used in various experiments by scientists such as Benjamin Franklin and Charles-Augustin de Coulomb to explore the nature of electric charges and forces. - Atmospheric Electricity:
Electroscopes have been used in atmospheric research to study atmospheric electricity and the behaviour of charges in the atmosphere, especially during thunderstorms and other weather phenomena. - Assessing Charge Distribution:
In some scientific experiments, electroscope measurements are used to assess the distribution of charge on objects and to study electrostatic phenomena. - Qualitative Charge Detection:
Electrometers can be used to determine the qualitative distribution of electric charge on different objects or materials.
Theory
- The principle of an electroscope is based on the atomic structure of elements, the internal structure of metal elements, charge induction and the idea that like charges repel and opposite charges attract. All elements are composed of electrons, protons and neutrons- with the electrons surrounding the nucleus. In metals these outer electrons are loosely held by the nuclei and are relatively free to move within the material.
- An electroscope has a metal detector knob on top which is connected to a pair of metal leaves hanging from the bottom of the connecting rod.
- When no charge is present the metal leaves hang loosely downward. However, if an object wth a charge is brought near the electroscope one of the two things can happen.
- If the charge is positive electrons in the metal of the electroscope are attracted to the charge, and move upwards out of the leaves. This causes a temporary positive charge and because like charges repel, the leaves separate.
- When the charge is removed, the electrons return to their original positions and leaves relax.
- So an electroscope reacts to the presence of a charge through the movements of electrons either into or away from the leaves.
- In either case the leaves separate but the electroscope cannot tell if the charge or a negative charge- it is only responding to the presence of an electrical charge
Material Required
- Glass jar with a lid
- 2 Inch of plastic straw
- 5 Inch of 14 gauge copper wire
- Hot glue
- Pliers
- Balloon
- Two 2 Inch square pieces of aluminium foil
Procedure
- Start by punching a hole in the jar lid large enough for the straw and the copper wire to fit through. Insert the straw into the hole and center it, leave a couple of inches of space from the bottom of the jar. Use the hot glue to secure the straw in place.
- Next, insert the copper wire into the straw, with about 2 inch protruding from the straw inside the jar.
- Use the pliers to bend 1 inch of the copper wire into a hook to hold the aluminum foil later.
- Use the pliers to bend the remaining copper on top of the lid into a coil to provide more surface area.
- Next, cut a small slit in the aluminum foil and slide them onto the copper hook.
- Attach the lid to the jar.
- Now, rub the balloon on your head.
- Place the balloon next to the copper coils. Observe what happens to the metal inside the jar.
- Move the material away and touch your hand to the coiled wire. Observe what happens.
- Repeat steps 8 to 10 with any other materials you would
like to test.
Observation
- As the charged comb approaches the metal rod, the leaves inside the container start to separate and repel each other. This is a clear indication that they have acquired a similar charge and are trying to move away from each other.
- When the charged comb is removed, the leaves return to their original position, indicating that the charge has dissipated, and the leaves have neutralized.
- If you touch the metal rod with a charged object (e.g., the charged comb), the leaves will diverge even more due to the transfer of charge. However, if the charge is opposite in nature, the leaves will collapse, showing an attraction between them.
Conclusion
Electroscope is an effective tool for detecting and studying electric charges. By constructing a working model of this device and conducting the experiment, we observed how the leaves respond to the presence of electric charges. The leaves diverged when exposed to a like charge and collapsed when exposed to an opposite charge. This experiment helps to illustrate the basic principles of electrostatics and provides a simple yet insightful way to visualize electric charge interactions.
Project PDF Download Link:

