
Ready to Serve!

Ready to Serve!
Foaming Capacity of Soaps Chemistry Investigatory Project PDF
[PDF Download link Given Below]
To get the link Scroll down to bottom of this Article
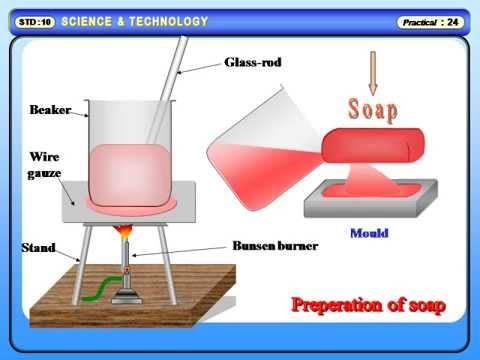
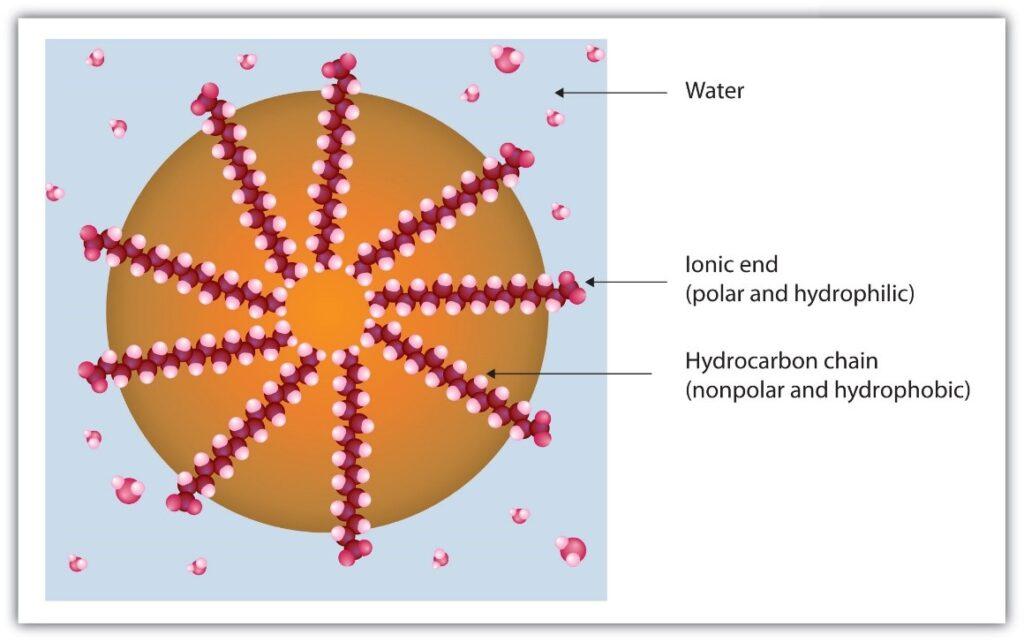
Soaps are sodium or potassium salts of higher fatty acids like stearic, palmitic and oleic acids can be either saturated or unsaturated. They contain a long hydrocarbon chain of about 10-20 carbon with one carboxylic acid group as the functional group. A soap molecule a tadpole shaped structure, whose ends have different polarities. At one end is the long hydrocarbon chain that is non- polar and hydrophobic, i.e., insoluble in water but oil soluble. At the other end is the short polar carboxylate ion which is hydrophilic i.e., water soluble but insoluble in oil and grease. Long Hydrocarbon Chain contain Hydrophobic and Hydrophilic end. When soap is shaken with water it becomes a soap solution that is colloidal in nature. Agitating it tends to concentrate the solution on the surface and causes foaming. This helps the soap molecules make a unimolecular film on the surface of water and to penetrate the fabric. The long non-polar end of a soap molecule that are hydrophobic, gravitate towards and surround the dirt (fat or oil with dust absorbed in it). The short polar end containing the carboxylate ion, face the water away from the dirt. A number of soap molecules surround or encircle dirt and grease in a clustered structure called ‘micelles’, which encircles such particles and emulsify them. Cleansing action of soaps decreases in hard water. Hard water contains Calcium and magnesium ions which react with sodium carbonate to produce insoluble carbonates of higher fatty acids. This hardness can be removed by addition of Sodium Carbonate.
The most popular soap making process today is the cold process method, where fats such as olive oil react with strong alkaline solution, while some soapers use the historical hot process. Handmade soap differs from industrial soap in that, usually, an excess of fat is sometimes used to consume the alkali (super fatting), and in that the glycerine is not removed, leaving a naturally moisturizing soap and not pure detergent. Often, emollients such as jojoba oil or Shea butter are added ‘at trace’ (the point at which the saponification process is sufficiently advanced that the soap has begun to thicken), after most of the oils have saponified, so that they remain unreacted in the finished soap.
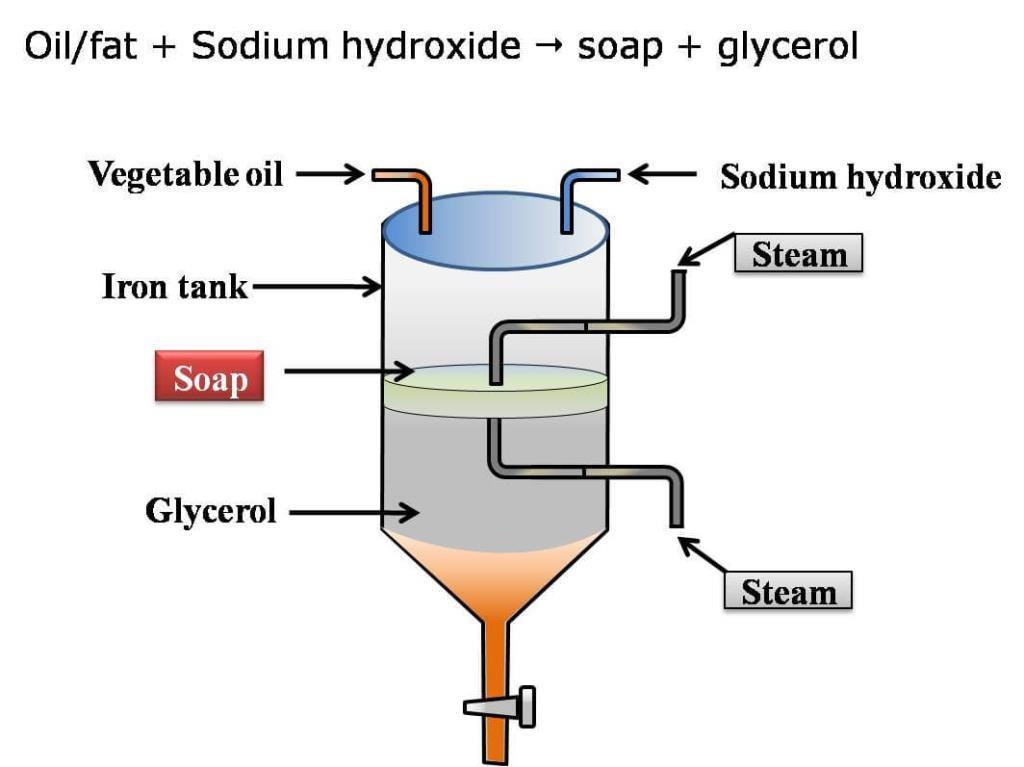
Soap is derived from either vegetable or animal fats. Sodium Tallowate, a common ingredient in much soap, is derived from rendered beef fat. Soap can also be made of vegetable oils, such as palm oil, and the product is typically softer. An array of specifiable oils and fats are used in the process such as olive, coconut, palm, cocoa butter to provide different qualities. For example, olive oil provides mildness in soap; coconut oil provides lots of lather; while coconut and palm oils provide hardness. Sometimes castor oil can also be used as an ebullient. Smaller amounts of unsaponifiable oils and fats that do not yield soap are sometimes added for further benefits.
In cold-process and hot-process soap making, heat may be required for saponification. Cold-process soap making takes place at a sufficient temperature to ensure the liquification of the fat being used. Unlike cold-processed soap, hot-processed soap can be used right away because the alkali and fat saponify more quickly at the higher temperatures used in hot-process soap making. Hot-process soap making was used when the purity of alkali was unreliable. Cold-process soap making requires exact measurements of alkali and fat amounts and computing their ratio, using saponification charts to ensure that the finished product is mild and skin-friendly.
Hot process:
In the hot-process method, alkali and fat are boiled together at 80–100 °C until saponification occurs, which the soap maker can determine by taste or by eye. After saponification has occurred, the soap is sometimes precipitated from the solution by adding salt, and the excess liquid drained off. The hot, soft soap is then spooned into a mould.
Cold process:
A cold-process soap maker first looks up the saponification value of the fats being used on a saponification chart, which is then used to calculate the appropriate amount of alkali. Excess unreacted alkali in the soap will result in a very high pH and can burn or irritate skin. Not enough alkali and the soap are greasy. The alkali is dissolved in water. Then oils are heated, or melted if they are solid at room temperature. Once both substances have cooled to approximately 100-110°F (37-43°C), and are no more than 10°F (~5.5°C) apart, they may be combined. This alkali-fat mixture is stirred until “trace”. There are varying levels of trace. After much stirring, the mixture turns to the consistency of a thin pudding. “Trace” corresponds roughly to viscosity. Essential and fragrance oils are added at light trace. Introduction to the experiment Soap samples of various brands are taken and their foaming capacity is noticed. Various soap samples are taken separately and their foaming capacity is observed. The soap with the maximum foaming capacity is thus, said to be having the best cleaning capacity.
Soap samples of various brands are taken and their foaming capacity is noticed. Various soap samples are taken separately and their foaming capacity is observed. The soap with the maximum foaming capacity is thus, said to be having the best cleaning capacity. The test requires to be done with distilled water as well as with tap water. The test of soap on distilled water gives the actual strength of the soaps cleaning capacity. The second test with tap water tests the effect of Ca2+ and Mg2+ salts on their foaming capacities.
OBJECTIVE:
To compare the foaming capacity of various soaps.
The foaming capacity of soap depends upon the nature of the soap and its concentration. This may be compared by shaking equal volumes of solutions of different samples having the same concentration with same force for the same amount of time. The solutions are then allowed to stand when the foam produced during shaking disappears gradually. The time taken for the foam to disappear in each sample is determined. The longer the time taken for the disappearance of the foam for the given sample of soap, greater is its foaming capacity or cleansing action.
Apparatus Requirements:
Five 100ml conical flasks, five test tubes, 100ml measuring cylinder, test tube stand, weighing machine, stop watch.
Chemical Requirements:
Five different soap samples, distilled water, tap water.
4. Close the mouth of the test tube and shake vigorously for a minute. Do the same for all test tubes and with equal force.
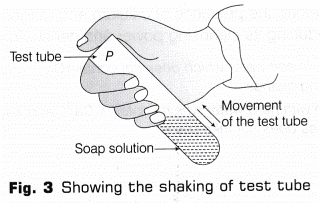
5. Start the timer immediately and notice the rate of disappearance of 2mm of froth.
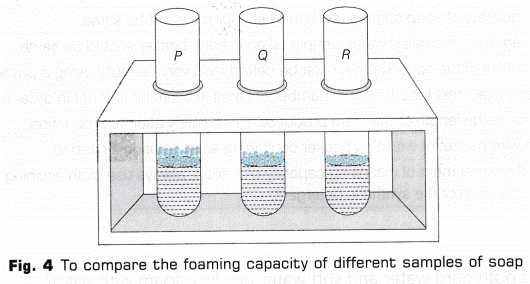
6. Record the observation in tabular form
The following outcomes were noticed at the end of the experiment
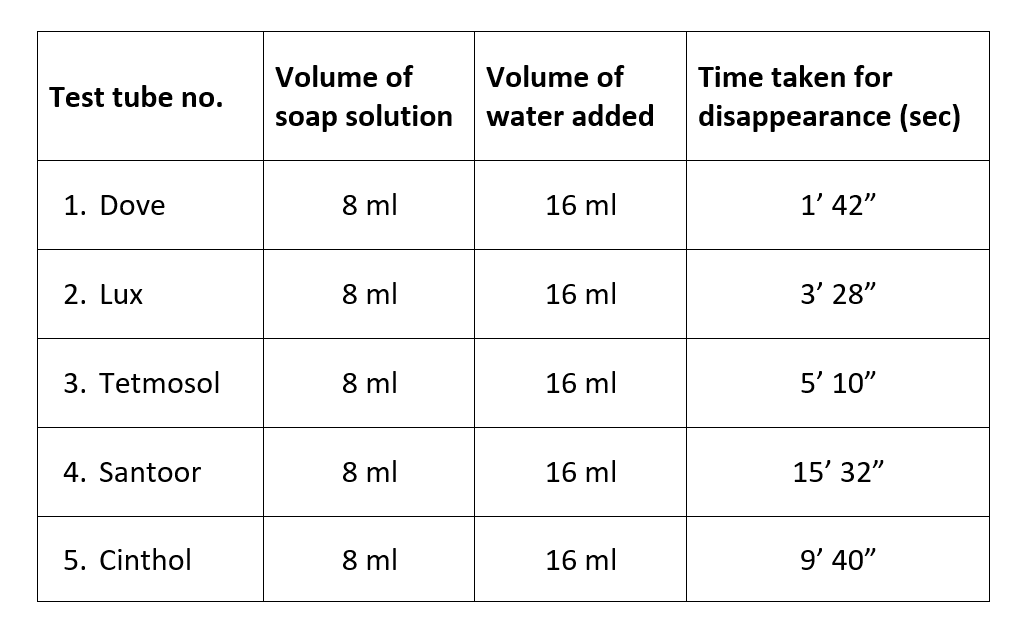
The cleansing capacity of the soaps taken is in the order:
Santoor > Dove > Cinthol > Tetmosol > Lux
From this experiment, we can infer that Santoor has the highest foaming capacity, in other words, highest cleaning capacity. Lux, on the other hand is found to have taken the least amount of time for the disappearance of foam produced and thus is said to be having the least foaming capacity and cleansing capacity.

The tests show negative results for the presence of the salts causing hardness in water. The water used does not contain salts of Ca2+ and Mg2+. The tap water provided is soft and thus, the experimental results and values hold good for distilled water and tap water.
Books:
Lab Manual Chemistry-XII
Comprehensive Chemistry – 12
Internet sources:
www.wikipedia.org
www.google.com
www.yahoo.com
https://www.icbse.com
Foaming Capacity of Soaps Chemistry Investigatory Project PDF Download Link