Methods of Water Purification Chemistry Investigatory Project PDF Class 12

Introdcution
Water purification is the process of removing undesirable chemicals, biological contaminants, suspended solids and gases from contaminated water. The goal is to produce water fit for a specific purpose. Most water is purified for human consumption (drinking water), but water purification may also be designed for a variety of other purposes, including meeting the requirements of medical, pharmacological, chemical and industrial applications. In general, the methods used include physical processes such as filtration, sedimentation, and distillation, biological processes such as filters or biologically active carbon, chemical processes such as flocculation and chlorination and the use of electromagnetic radiation such as ultraviolet light. The purification process of water may reduce the concentration of particulate matter including suspended particles, parasites, bacteria, algae, viruses, fungi and a range of dissolved and particulate material derived from the surfaces that water may have contacted after falling as rain. The standards for drinking water quality are typically set by governments or by international standards. These standards will typically set minimum and maximum concentrations of contaminants for the use that is to be made of the water. It is not possible to tell whether water is of an appropriate quality by visual examination. Simple procedures such as boiling or the use of a household activated filter are not sufficient for treating all the possible contaminants that may be present in water from an unknown source. Even natural spring – considered safe for all practical purposes in the 19th century – must now be tested before determining what kind of treatment, if any, is needed. Chemical and microbiological analysis, while expensive, are the only way to obtain the information necessary for deciding on the appropriate method of purification. According to a 2007 World Health Organization (WHO) report, 1.1 billion people lack access to an improved drinking water supply, 88 percent of the 4 billion annual cases of diarrheal disease are attributed to unsafe water and inadequate sanitation and hygiene, and 1.8 million people die from diarrheal diseases each year. The WHO estimates that 94 percent of these diarrheal cases are preventable through modifications to the environment, including access to safe water. Simple techniques for treating water at home, such as chlorination, filters, and solar disinfection, and storing it in safe containers could save a huge number of lives each year. Reducing deaths from waterborne diseases is a major public health goal in developing countries.
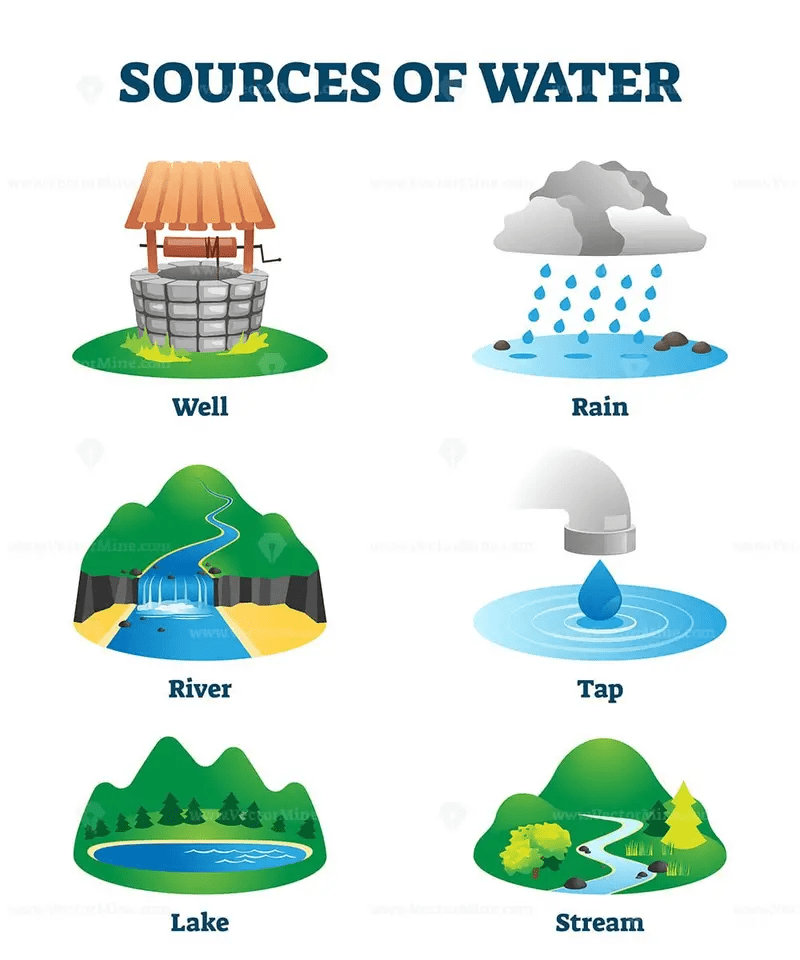
Sources of Water
- Groundwater: The water emerging from some deep ground water may have fallen as rain many tens, hundreds, or thousands of years ago. Soil and rock layers naturally filter the ground water to a high degree of clarity and often it does not require additional treatment other than adding chlorine or chloramines as secondary disinfectants. Such water may emerge as springs, artesian, or may be extracted from boreholes or wells. Deep ground water is generally of very high bacteriological quality (i.e., pathogenic bacteria or the pathogenic protozoa are typically absent), but the water may be rich in dissolved solids, especially carbonates and sulphates of calcium and magnesium. Depending on the strata through which the water has flowed, other ions may also be present including chloride, and bicarbonate. There may be a requirement to reduce the iron or manganese content of this water to make it acceptable for drinking, cooking, and laundry use. Primary disinfection may also be required. Where groundwater recharge is practised (a process in which river water is injected into an aquifer to store the water in times of plenty so that it is available in times of drought), the groundwater may require additional treatment depending on applicable state and federal regulation.
- Upland lakes and reservoirs: Typically located in the headwaters of river systems, upland reservoirs are usually sited above any human habitation and may be surrounded by a protective zone to restrict the opportunities for contamination. Bacteria and pathogen levels are usually low, but some bacteria, protozoa or algae will be present. Where uplands are forested or peaty,humic acids can colour the water. Many upland sources have low pH which require adjustment.
- Rivers, canals and low land reservoirs: Low land surface waters will have a significant bacterial load and may also contain algae, suspended solids and a variety of dissolved constituents.
- Atmospheric water generation is a new technology that can provide high quality drinking water by extracting water from the air by cooling the air and thus condensing water vapour.
- Rainwater harvesting or fog collection which collects water from the atmosphere can be used especially in areas with significant dry seasons and in areas which experience fog even when there is little rain.
- Desalination of seawater by distillation or reverse osmosis.
Boiling
Boiling water is used as a method of making it potable by killing microbes and viruses that may be present. The sensitivity of different micro-organisms to heat varies, but if water is held at 100 °C (212°F) for one minute, most micro-organisms and viruses are in activated. In places having proper water purification system, it is recommended only as an emergency treatment method or for obtaining potable water in the wilderness or in rural areas, as it cannot remove chemical toxins or impurities. The traditional advice of boiling water for ten minutes is mainly for additional safety, since microbes start getting eliminated at temperatures greater than 60° (140°F) and bringing it to its boiling point is also a useful indication, the water is disinfected.
Filtration
In the water industry, clarified water is the goal of the filtering. It is primarily used for storm water, wastewater, and drinking water applications, but it also has uses in industrial manufacturing, power plants, food and beverage production facilities, mining and other heavy-duty applications.
Water filtration can remove or reduce the concentration of suspended particles, parasites, bacteria, algae, viruses, fungi, and more chemical and biological contaminants.
In order for water to be filtered, it can only pass through the filter medium if some driving force is applied, which may be caused by gravity, centrifugation, application of pressure on the fluid above the filter, or other processes that use pumps, valves and pipes to produce enough pressure to push the water through the filter.
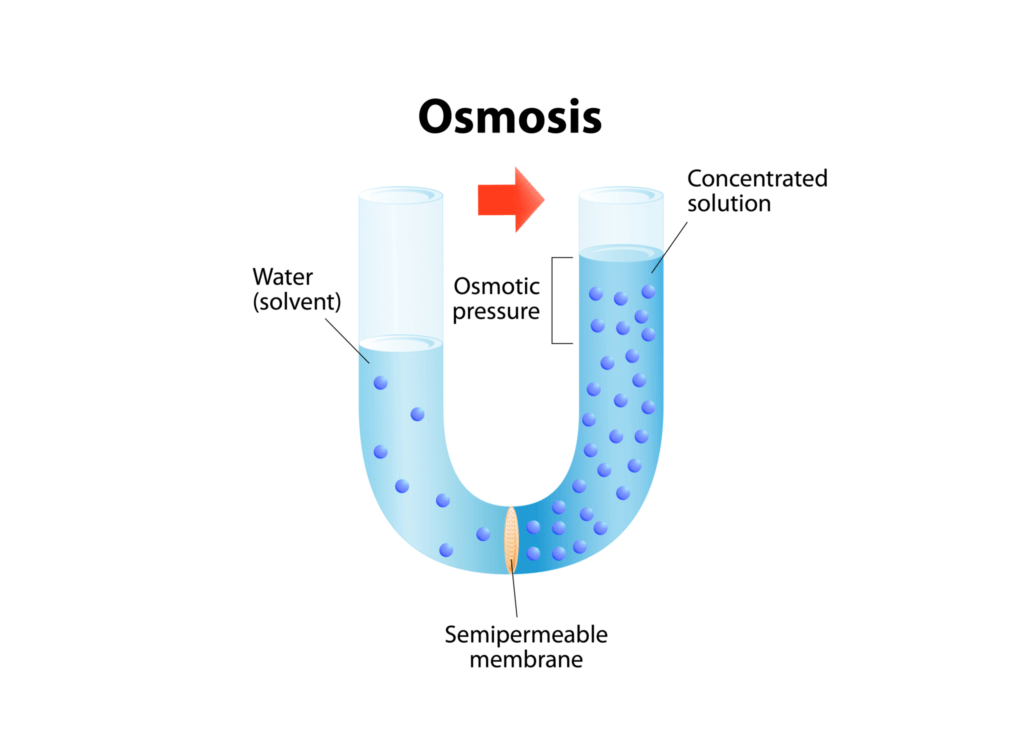
Reverse Osmosis
Reverse Osmosis is a water purification process that uses a semi-permeable membrane to filter out unwanted molecules and large particles such as contaminants and sediments like chlorine, salt, and dirt from drinking water. In reverse osmosis, an applied pressure is used to overcome the osmotic pressure and push the water from high concentration to low concentration of contaminants. This means it’s being forced in reverse and the contaminated water is trying to move into the pure water, but because it must pass through a filter first, the contaminants get trapped and only the pure water passes through resulting in the cleanest possible drinking water.reverse osmosis differs from carbon filtration in that it can rid the water of up to 99% of all contaminants and sediments, or particles as small as 1 micron. It would be best to get a reverse osmosis filtration system to safeguard that your water is contaminant-free.
Water Chlorination
Water chlorination is the process of adding chlorine or chlorine compounds such as sodium hypochlorite to water. This method is used to kill bacteria, viruses and other microbes in water. In particular, chlorination is used to prevent the spread of water borne diseases such as cholera, dysentery, and typhoid. As a halogen, chlorine is a highly efficient disinfectant, and is added to public water supplies to kill disease-causing pathogen, such as bacteria, viruses and protozoans, that commonly grow in water supply reservoirs, on the walls of water mains and in storage tank. As a strong oxidizing agent, chlorine kills via the oxidation of organic molecules. Chlorine and the hydrolysis product hypochlorous acid are not charged and therefore easily penetrate the negatively charged surface of pathogens. It is also to disintegrate the lipids that compose the cell wall and react with intracellular enzymes and proteins, making them non-functional. Microorganisms then either die or are no longer able to multiply.
UV Water Purification
UV water purification systems purify water by using ultra violet rays to kill microorganisms present in the water. UV rays completely kill water-borne microorganisms and prevent their reproduction by disrupting their DNA. Also, UV rays do not lead to chemical changes in the water. As such, water purified from UV rays doesn’t contain any harmful microorganisms and retain their original taste. Modern water purifiers use low-pressure mercury vapor lamps which produce ultra violet radiation at a specific level. The mercury vapor lamps are installed in such a way that they do not contact water. One of the biggest advantages of using a UV water purifier is instant purification of water. UV water purification systems do not use any chemicals. UV water purifiers are cost-effective; the mercury vapor lamp of the appliance is similar to a standard light bulb in terms of power consumption and price. UV water purifiers can last long, especially if you regularly maintain the appliance.
Ozone Disinfection
Ozone disinfection Ozone is an unstable molecule which readily gives up one atom of oxygen providing a powerful oxidizing agent which is toxic to most waterborne organisms. It is a very strong, broad spectrum disinfectant that is widely used in Europe. It is an effective method to inactivate harmful protozoa that form cysts. It also works well against almost all other pathogens. Ozone is made by passing oxygen through ultraviolet light or a “cold” electrical discharge. To use ozone as a disinfectant, it must be created on-site and added to the water by bubble contact. Some of the advantages of ozone include the production of fewer dangerous by-products and the absence of taste and odour problems (in comparison to chlorination) . Although fewer by-products are formed by ozonation, it has been discovered that ozone reacts with bromide ions in water to produce concentrations of the suspected carcinogen bromated. Bromide can be found in fresh water supplies in sufficient concentrations to produce (after ozonation) more than 10 ppb of bromate — the maximum contaminant level established by the USEPA. Another advantage of ozone is that it leaves no residual disinfectant in the water. Ozone has been used in drinking water plants since 1906 where the first industrial ozonation plant was built in Nice, France. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has accepted ozone as being safe; and it is applied as an anti-microbiological agent for the treatment, storage, and processing of foods.
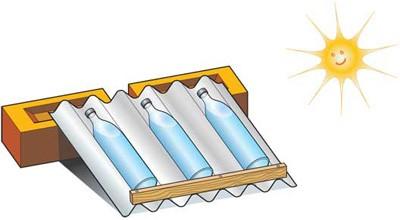
Solar Water Disinfection
One low-cost method of disinfecting water that can often be implemented with locally available materials is solar disinfection (SODIS). Unlike methods that rely on firewood, it has low impact on the environment. One recent study has found that the wild Salmonella which would reproduce quickly during subsequent dark storage of solar-disinfected water could be controlled by the addition of just 10 parts per million of hydrogen peroxide.
Benefits of Water Purification
Purification of water offers several advantages, primarily focused on ensuring that water is safe and suitable for various purposes, including drinking, cooking, and industrial processes. Some of the key advantages of water purification include:
- Removal of Contaminants: Water purification processes effectively remove contaminants such as bacteria, viruses, parasites, algae, fungi, minerals, and other impurities. This ensures that the water is safe for consumption and does not pose health risks.
- Disease Prevention: Purifying water helps prevent waterborne diseases caused by pathogens like bacteria and viruses. Access to clean water is crucial for public health, reducing the spread of waterborne illnesses such as cholera, typhoid, and dysentery.
- Improved Taste and Odour: Purification processes can enhance the taste and odour of water by eliminating unpleasant substances. This makes the water more palatable, encouraging increased consumption and promoting overall hydration.
- Protection of Ecosystems: Purification helps protect natural ecosystems by preventing the introduction of harmful pollutants and chemicals into water bodies. This is essential for maintaining the health of aquatic environments and preserving biodiversity.
- Prevention of Waterborne Chemical Contamination: Water purification removes or reduces the concentration of chemical pollutants, including heavy metals, pesticides, and industrial chemicals. This is vital for preventing the adverse health effects associated with exposure to these contaminants.
Conclusion
We can conclude from the project that there are various methods of purification of water. Today, we know that water is present everywhere on earth in different forms but due to human activities water is being polluted day by day not only that about 97% of earths water is in oceans which is not suitable for drinking or any other purpose. So, there is very small volume of water is left, to utilise that humans are using best ways to purify it. And in present time humans are capable to purify water and all the methods to purify it are mentioned in the project.
Precaution
- http://en.wikipedia.org
- www.google.com
- https://www.sciencedirect.com
- https://www.sciencebuddies.org
- https://atlas-scientific.com

